Electric vehicles (EVs) are changing the way we drive, offering a cleaner, quieter, and more efficient alternative to traditional gasoline-powered cars. However, one of the biggest questions new EV owners face is: how do I charge my vehicle efficiently and cost-effectively?
Understanding EV charging is crucial for maximizing convenience and reducing stress on the road. From different charging levels to installation costs and home setup options, knowing the details helps you enjoy your EV without surprises. This guide explains EV charging in a simple, practical way.
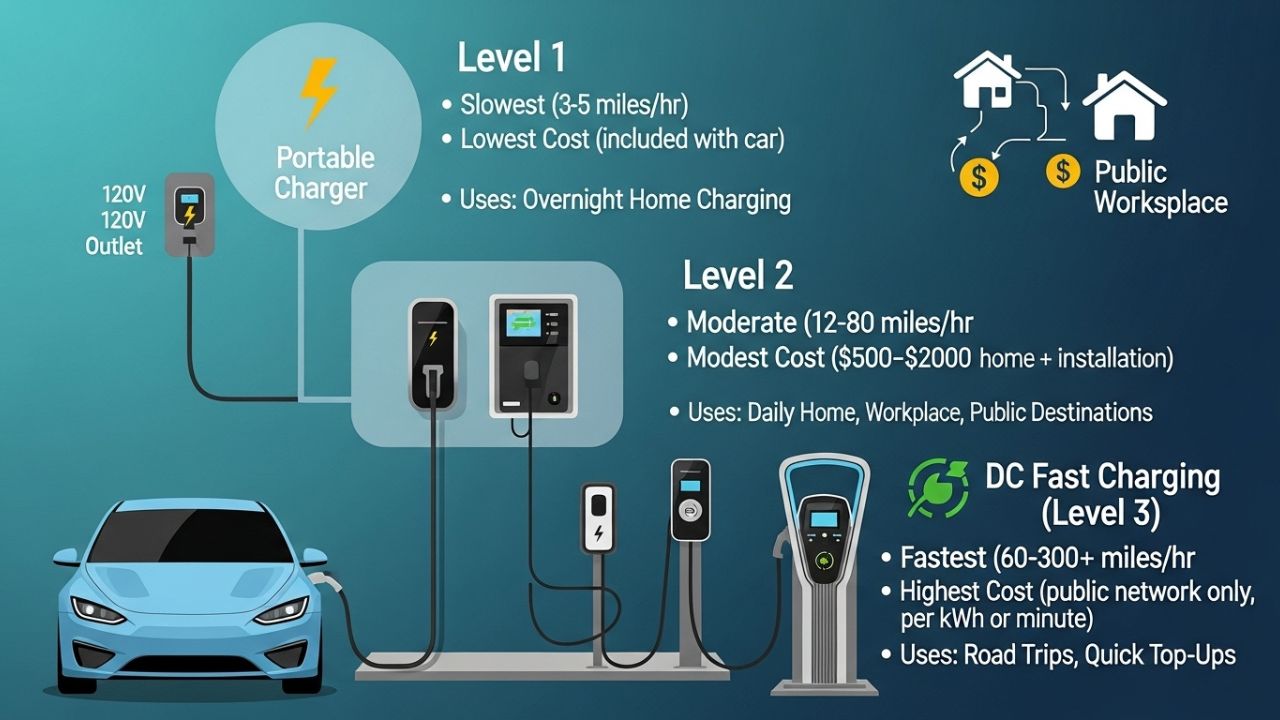
Understanding EV Charging Levels
EV chargers are categorized into three main levels, each with unique characteristics and use cases.
Level 1 Charging – Basic Home Charging
Level 1 charging uses a standard household outlet (120 volts). It’s slow but convenient for everyday use:
- Charging Speed: Adds about 3–5 miles of range per hour.
- Best Use: Overnight charging at home for drivers with short daily commutes.
- Pros: No special equipment required, minimal cost.
- Cons: Very slow; not practical for long trips.
Example: If you drive 30 miles a day, Level 1 charging can fully replenish your battery overnight without additional setup.
Level 2 Charging – Faster Home or Public Charging
Level 2 chargers operate at 240 volts, requiring a dedicated installation. They offer significantly faster charging than Level 1:
- Charging Speed: Adds 15–30 miles of range per hour.
- Best Use: Daily use, home charging, or public charging at workplaces.
- Pros: Faster charging, compatible with most EVs.
- Cons: Installation costs, requires professional setup.
Example: A full charge for a 60 kWh battery may take 6–8 hours, making it perfect for overnight or at-work charging.
Level 3 Charging / DC Fast Charging – Road Trip Friendly
Level 3 chargers, also known as DC fast chargers, provide rapid charging at high voltage. They are ideal for long-distance travel:
- Charging Speed: Can replenish 60–80% of battery in 20–40 minutes.
- Best Use: Highway charging and emergency top-ups.
- Pros: Extremely fast, convenient for long trips.
- Cons: More expensive, frequent use can slightly affect battery life, not practical for home use.
Example: On a 300-mile road trip, a DC fast charger can add over 200 miles in under half an hour while you grab a meal.
Read Also: Tesla Phone 2025? Starlink’s Spectrum Deal Explained — and Why There’s Still No “Model Pi”
EV Charging Costs
Charging an EV is typically cheaper than fueling a gas car, but the cost depends on where and how you charge.
Home Charging Costs
- Level 1: Very low cost; typically $1–$2 for 30 miles of range.
- Level 2: Slightly higher depending on electricity rates; roughly $5–$10 for a full 60 kWh battery.
Public Charging Costs
- Level 2 Public Chargers: Often free or $0.10–$0.30 per kWh.
- DC Fast Chargers: Usually $0.25–$0.50 per kWh, with some subscription options to reduce costs.
Tip: Charging at home during off-peak electricity hours can reduce costs even further.
Setting Up Home EV Charging
Home charging is convenient and gives you control over costs. Here’s how to get started:
Step 1: Assess Your Electrical System
- Confirm your home can support a 240V circuit for Level 2 chargers.
- Check breaker capacity; you may need an upgrade for larger chargers.
Step 2: Choose a Charger
- Select a charger compatible with your EV.
- Consider smart chargers with scheduling, energy monitoring, and mobile app control.
Step 3: Professional Installation
- Hire a licensed electrician to ensure safety and code compliance.
- Installation costs vary from $500–$2,000 depending on wiring and charger type.
Step 4: Plan for Future Needs
- If you plan to buy a second EV or a larger battery vehicle, consider installing a higher-capacity charger now.
- Smart chargers allow you to take advantage of lower electricity rates and optimize charging times.
Read Also: Mahindra Scorpio-N Petrol MT: Real Highway Mileage Tested and Latest Price Insights
Tips for Efficient EV Charging
- Charge overnight: Take advantage of off-peak electricity rates.
- Avoid unnecessary DC fast charging: Regular fast charging may slightly shorten battery lifespan.
- Monitor battery levels: Keeping your charge between 20–80% daily improves longevity.
- Use charging apps: Track cost, availability, and battery performance.
FAQs
1. How long does it take to fully charge an EV at home?
- Level 1: 12–24 hours depending on battery size.
- Level 2: 4–10 hours for a full charge.
2. Can I install a Level 2 charger myself?
- It’s safer to hire a certified electrician to comply with local codes.
3. Are fast chargers bad for the battery?
- Occasional use is fine, but frequent fast charging can slightly reduce long-term battery life.
4. How much does home charging cost per month?
- Driving 1,000 miles in a 60 kWh EV typically costs $50–$100 per month depending on local rates.
Conclusion
EV charging doesn’t have to be complicated. Understanding the different levels, costs, and home setup options allows you to plan efficiently and save money. Whether you rely on overnight home charging or take occasional fast-charging road trips, proper planning ensures convenience, cost-efficiency, and battery longevity.
With the right setup and habits, charging your EV can become a simple, stress-free part of daily life—leaving you more time to enjoy the quiet, smooth, and eco-friendly ride your electric vehicle provides.
1 thought on “EV Charging Explained: Levels, Costs, and Home Setup”